Custom Code Editor
Updated
In guided workflows, there are various scenarios where data needs to be transformed or refined before it can be effectively used by different components, nodes, or even brand-specific logic. For example, when an API response is received, the data often arrives in a raw or nested format that isn’t directly usable.
To address this, the Custom Code Editor allows you to write and execute Groovy scripts that can manipulate, extract, and reshape data. Whether you’re pulling out specific values from an API response, formatting data to match component expectations, or performing real-time computations, this editor plays a critical role in ensuring that data is workflow-ready.
Steps to Access the Custom Code Editor
Click the New Tab icon. Under the Sprinklr Service tab, select Guided Workflows within Resolve.
On the Guided Workflows window, click + Add Guided Workflow in the top right corner.
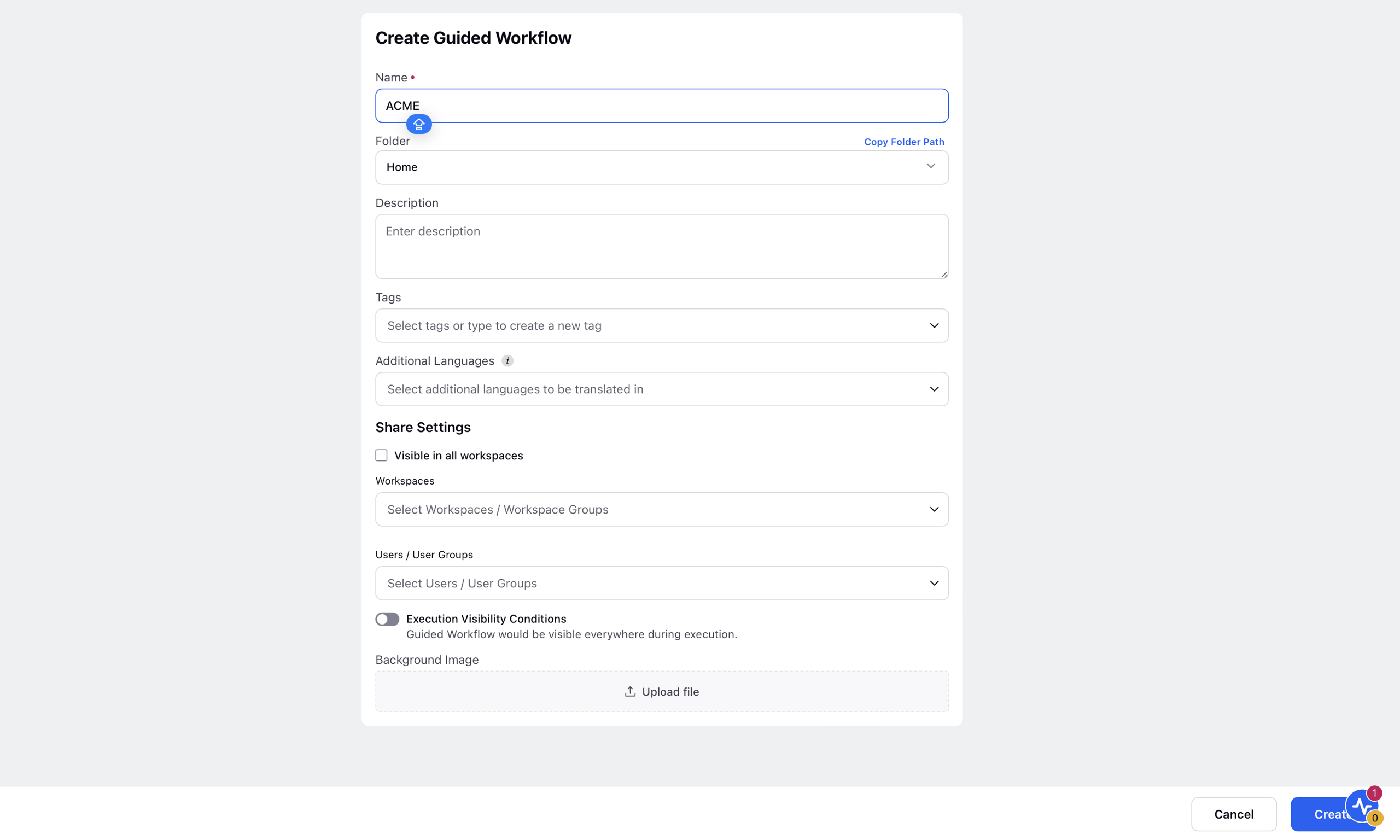
A Create Guided Workflow form will open up in which you can add your details and click Create in the bottom right corner.
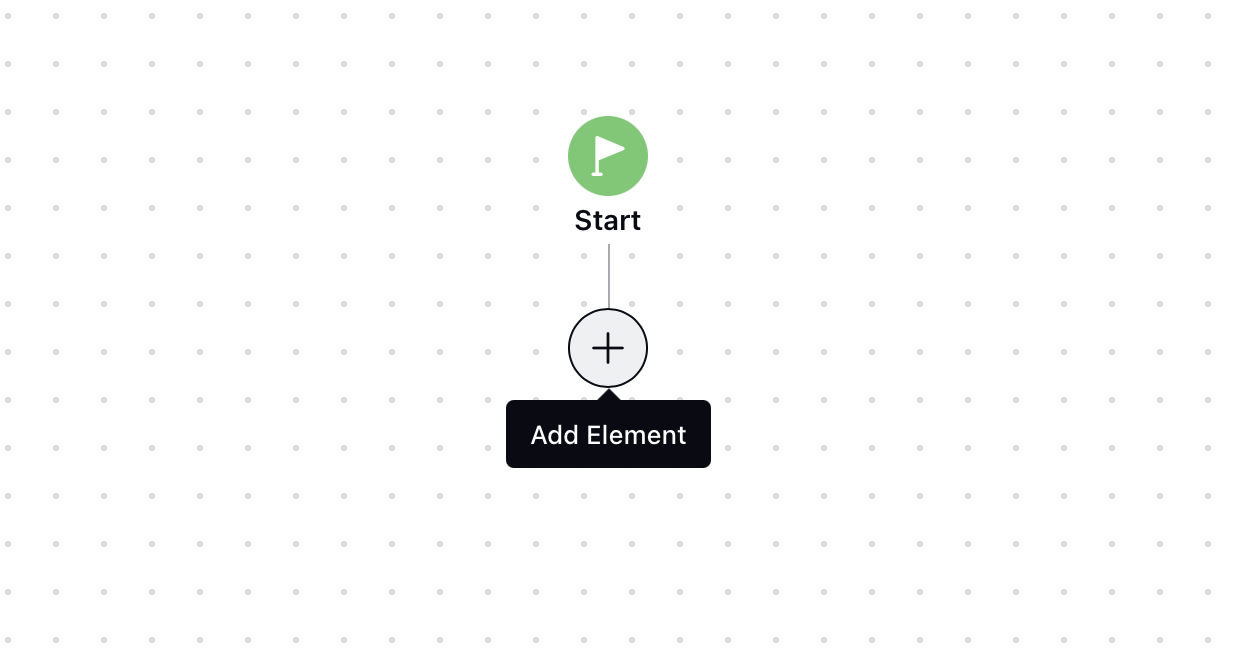
On the guided workflow canvas, click the Add Element icon and add an element containing the resource selector, such as Update Properties.
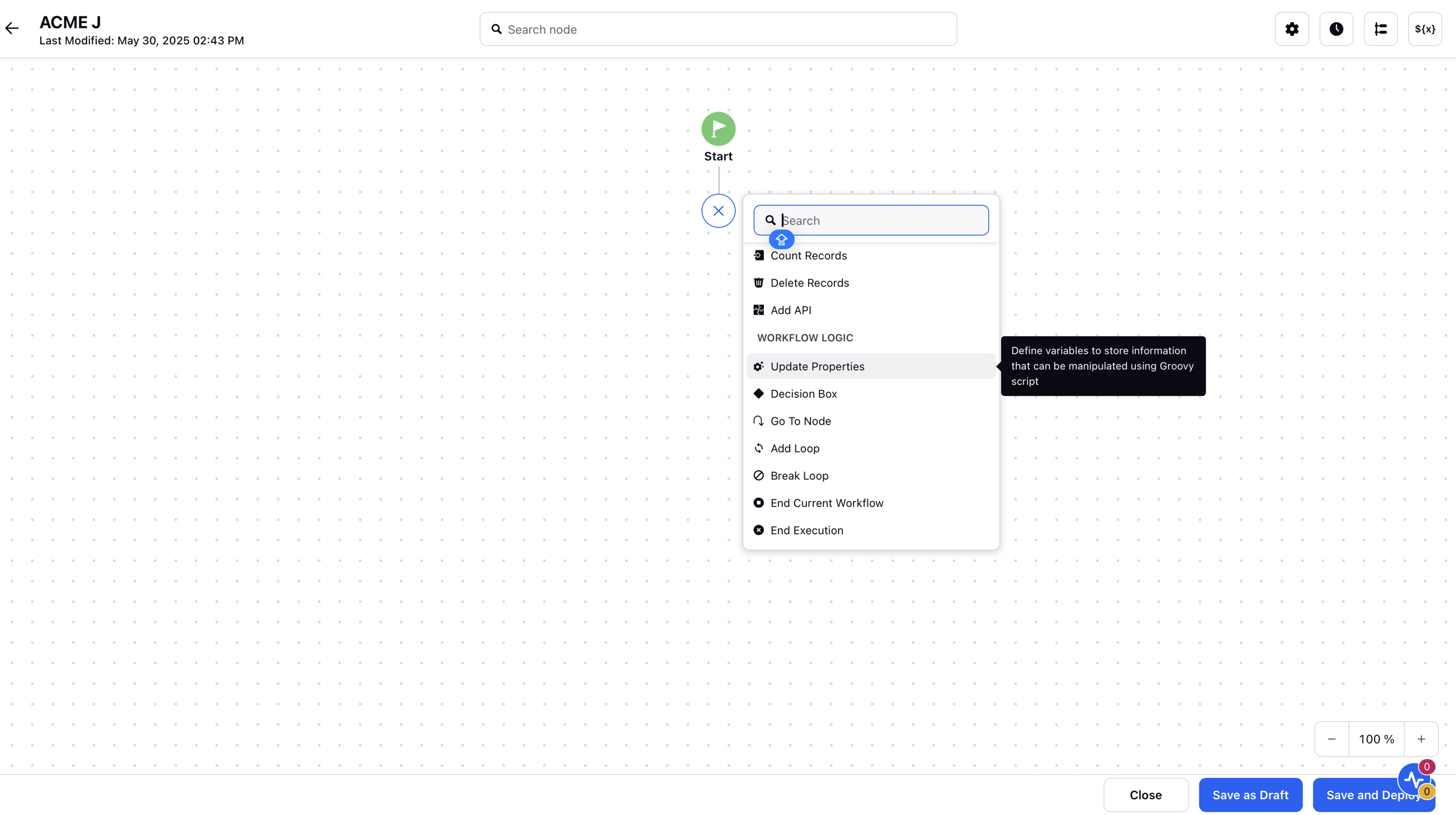
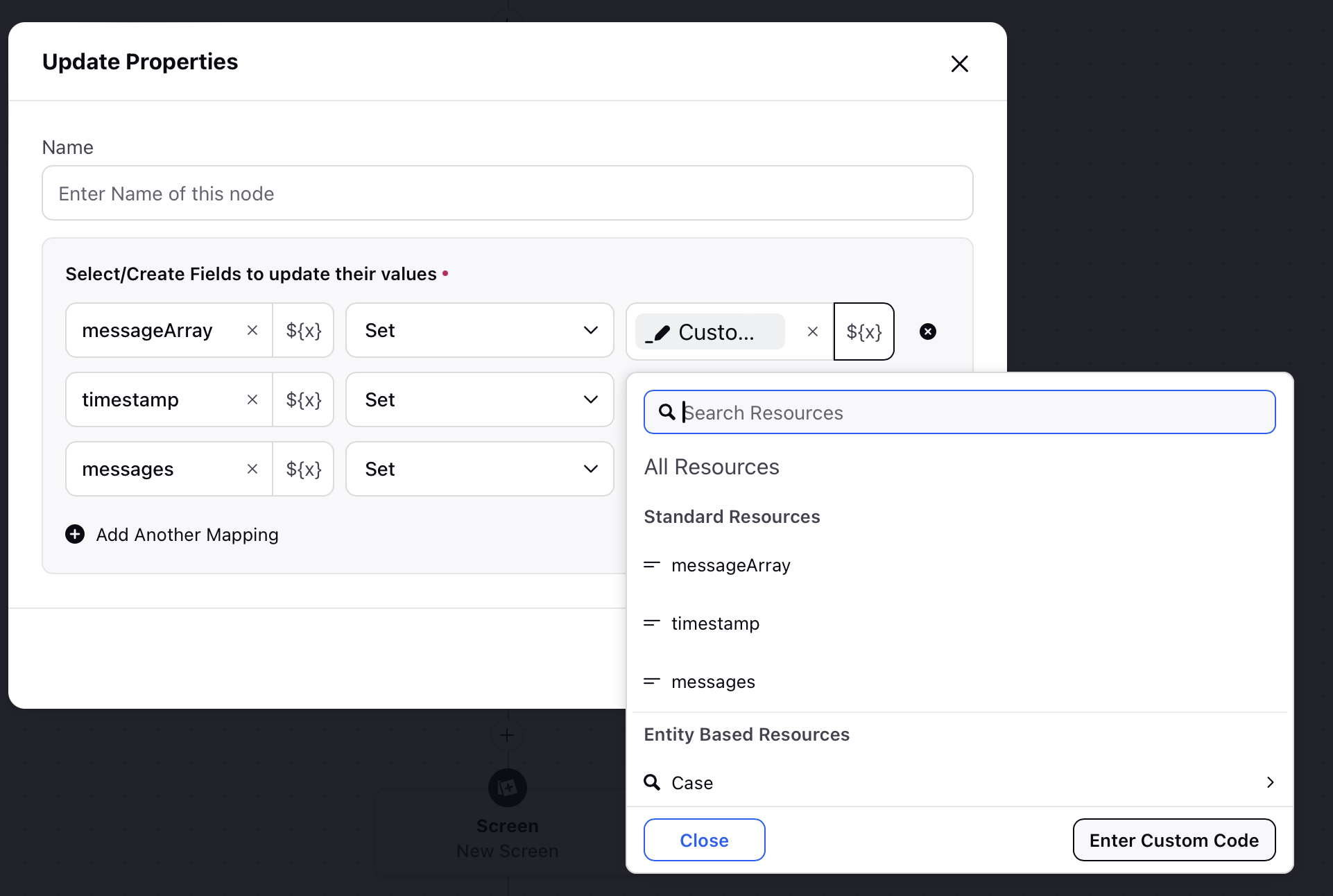
Navigate to Click to Select Resources, which for this instance is present in the Select/Create Fields to update their values field within the Update Properties window.
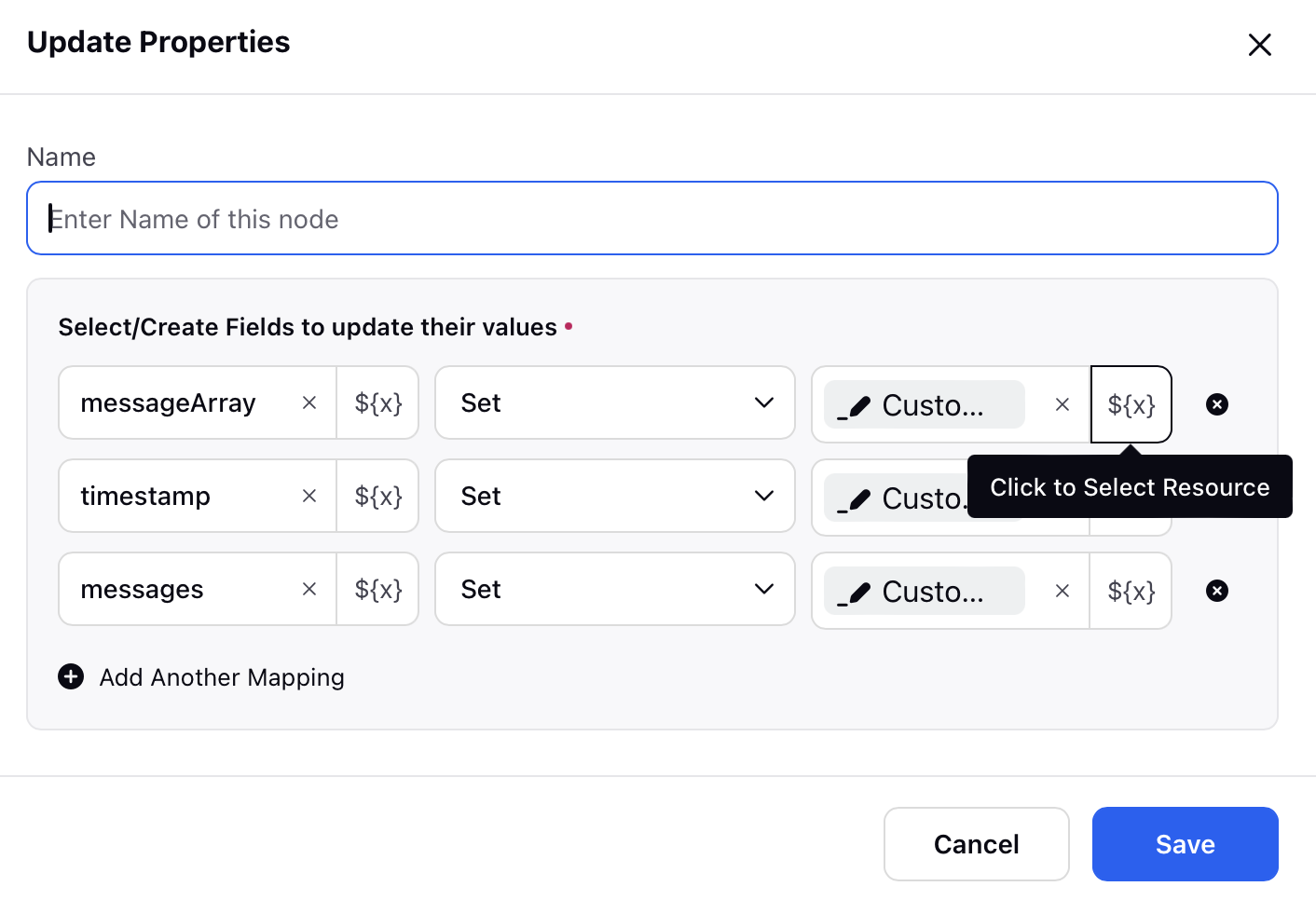
Click the Enter Custom Code button, and the Custom Code Editor will open.
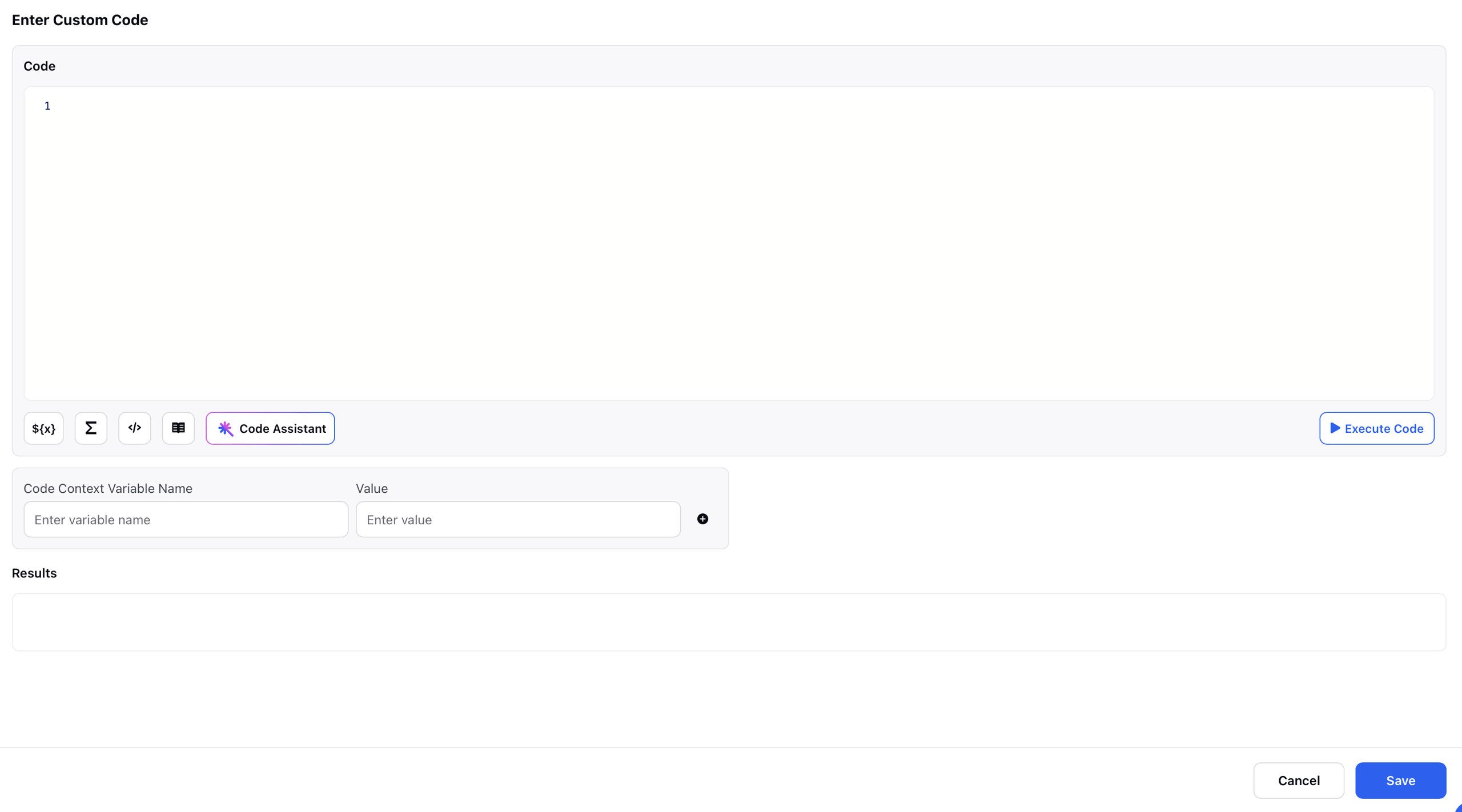
Key Components of the Custom Code Editor
The core idea of the Custom Code Editor is to allow users to manipulate data using Groovy scripts. Users can perform specific functions or transformations on the data within the editor, and the result of the script is returned and stored in a defined variable present, such as messageArray, for the given example, at the resource selector stage. This variable can then be referenced and reused across other components in the workflow, enabling a seamless flow of transformed data throughout the guided process.
Select Resources: This field allows users to access and select various resources available within the workflow. These resources can include standard entities or custom entities. By choosing a resource from this section, users can easily insert it into their custom Groovy script for data manipulation. This helps streamline the process of referencing dynamic data and ensures accurate, context-aware scripting within the Custom Code Editor.
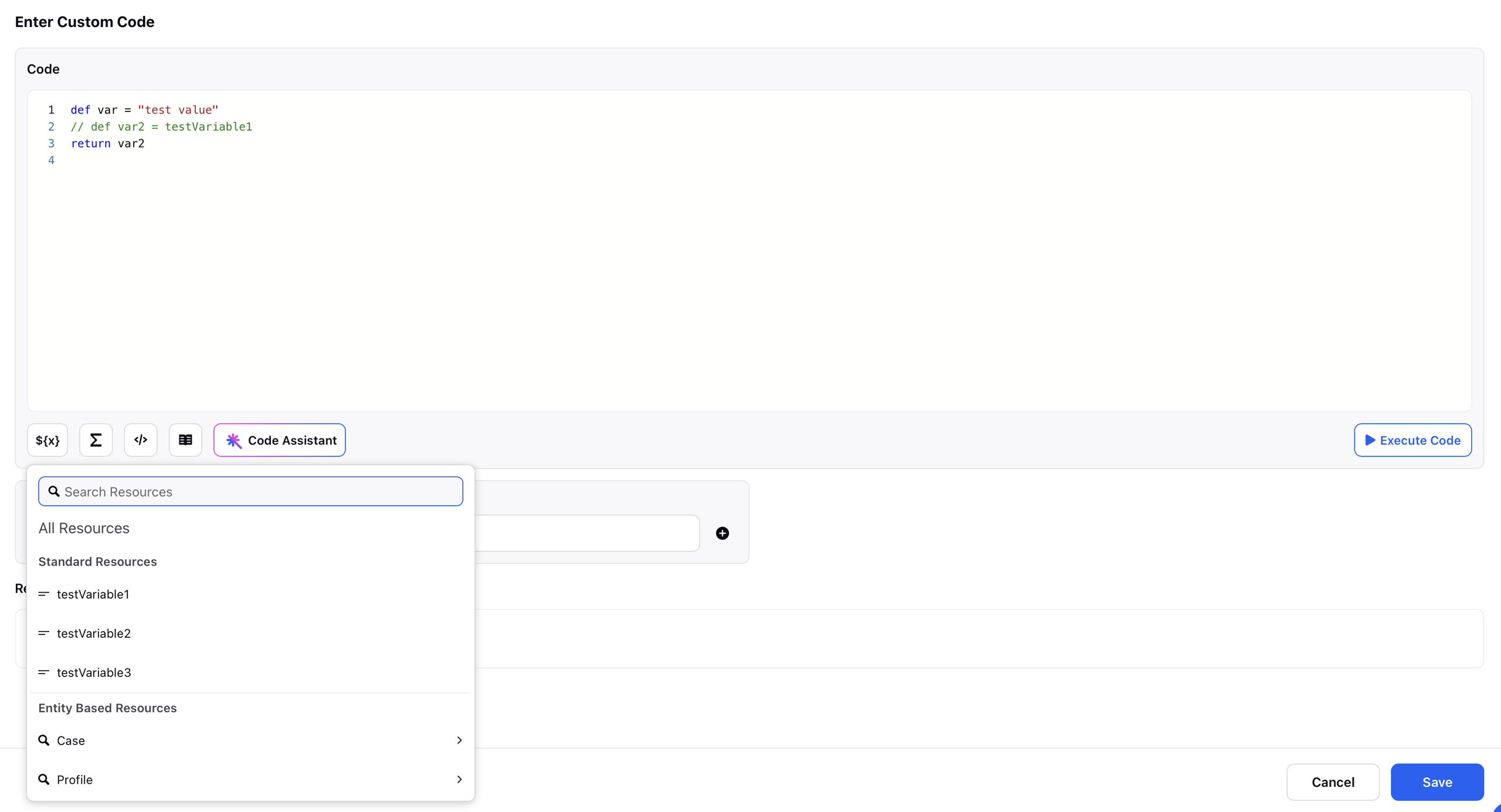
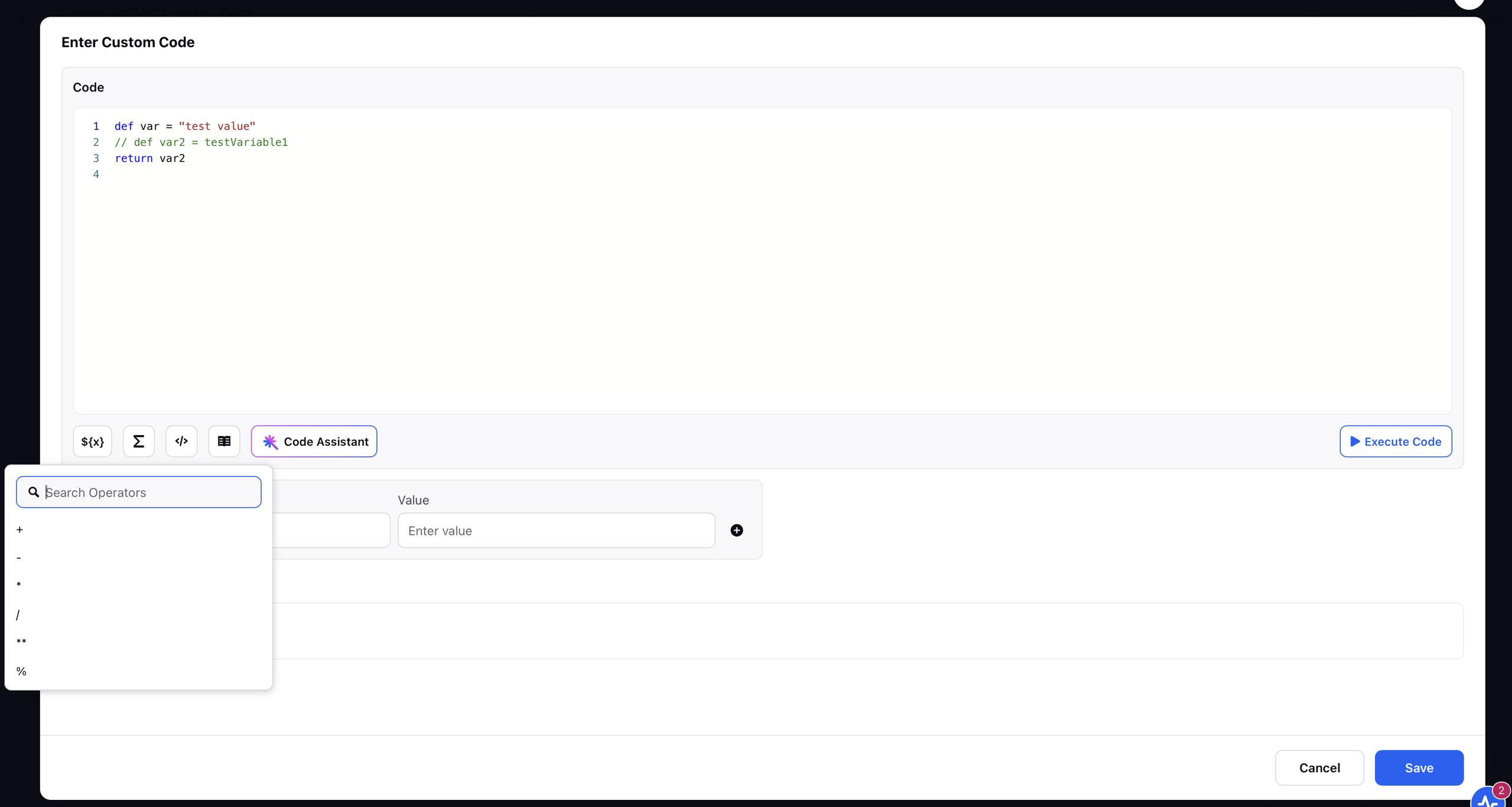
Select Operators:
This section provides a convenient list of common operators such as (addition), (subtraction), (modulus), and others. While these operators can always be typed manually using the keyboard, this panel serves as a quick-access reference to help users easily insert the appropriate symbols into their Groovy script, enhancing speed and reducing the chance of syntax errors.
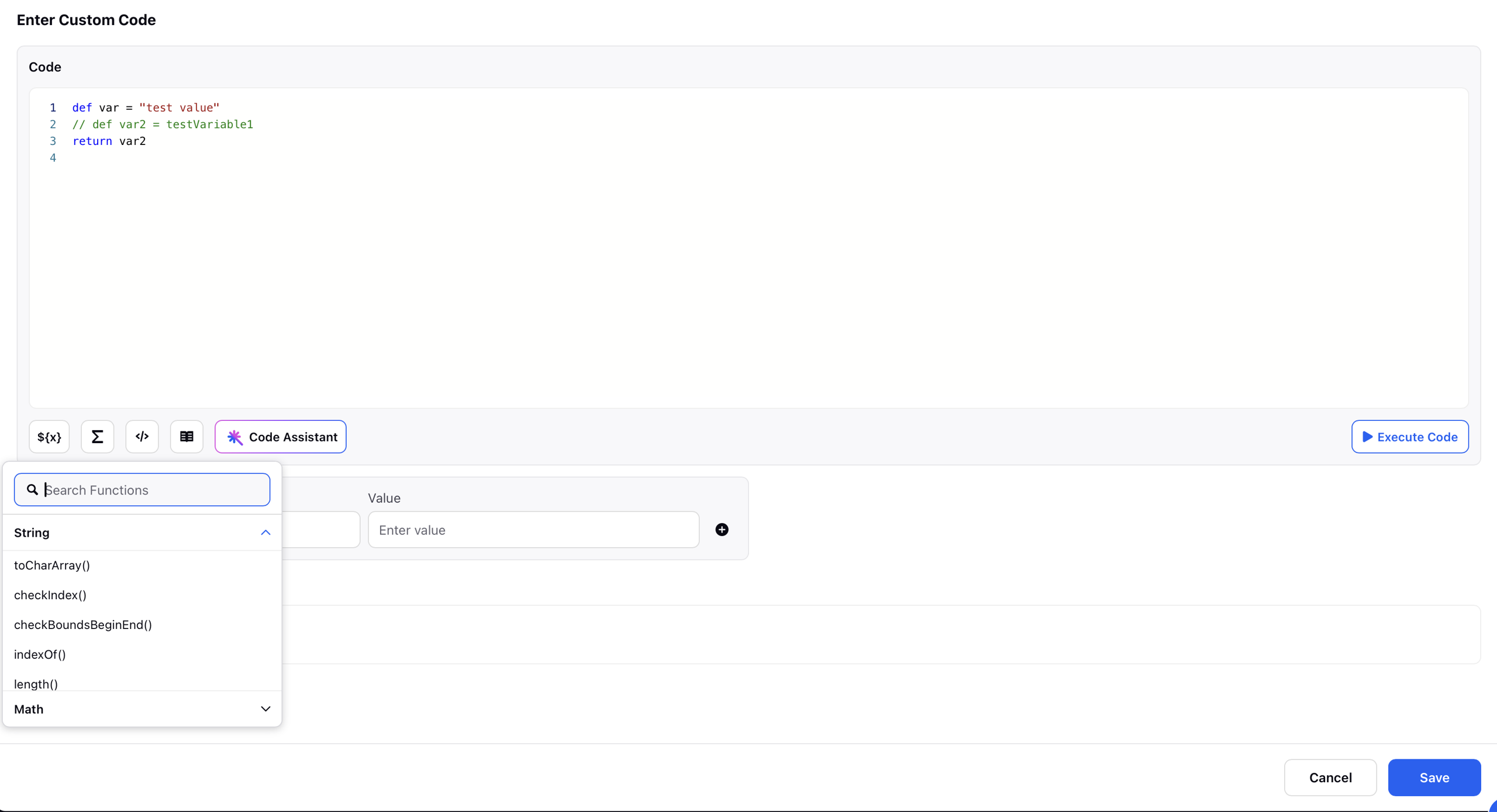
Functions: This section provides access to a comprehensive list of functions (also referred to as actions) available for use in Groovy scripting. It includes commonly used string, mathematical, and other utility functions that are compatible with the Custom Code Editor. A key feature of this section is that it not only lists the functions but also displays the correct syntax for each, helping users understand how to apply them effectively within their scripts.
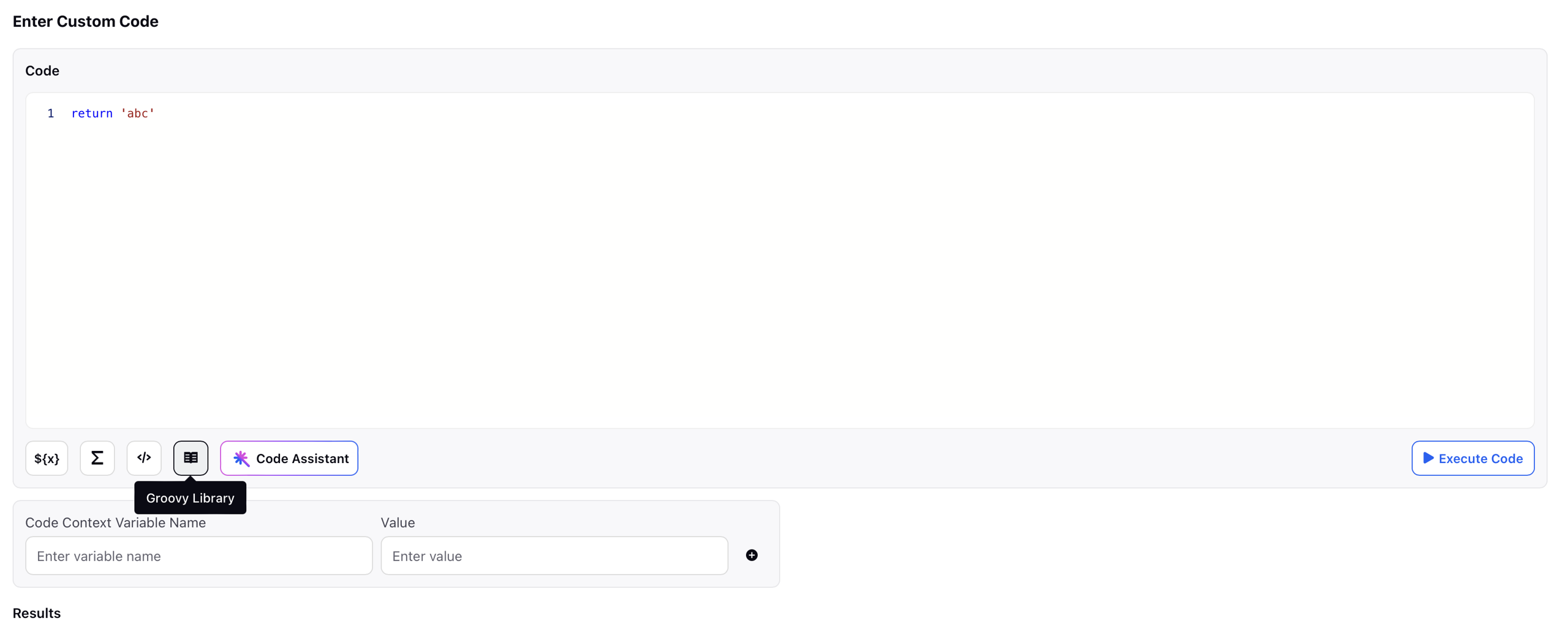
Groovy Library: This field provides a direct link to a Knowledge Base (KB) article that covers various aspects of Groovy scripting. It includes examples of Groovy functions, common use cases, and custom scripts that can be used within the Custom Code Editor. This resource serves as a helpful reference for users looking to explore advanced scripting techniques or troubleshoot specific implementation scenarios.
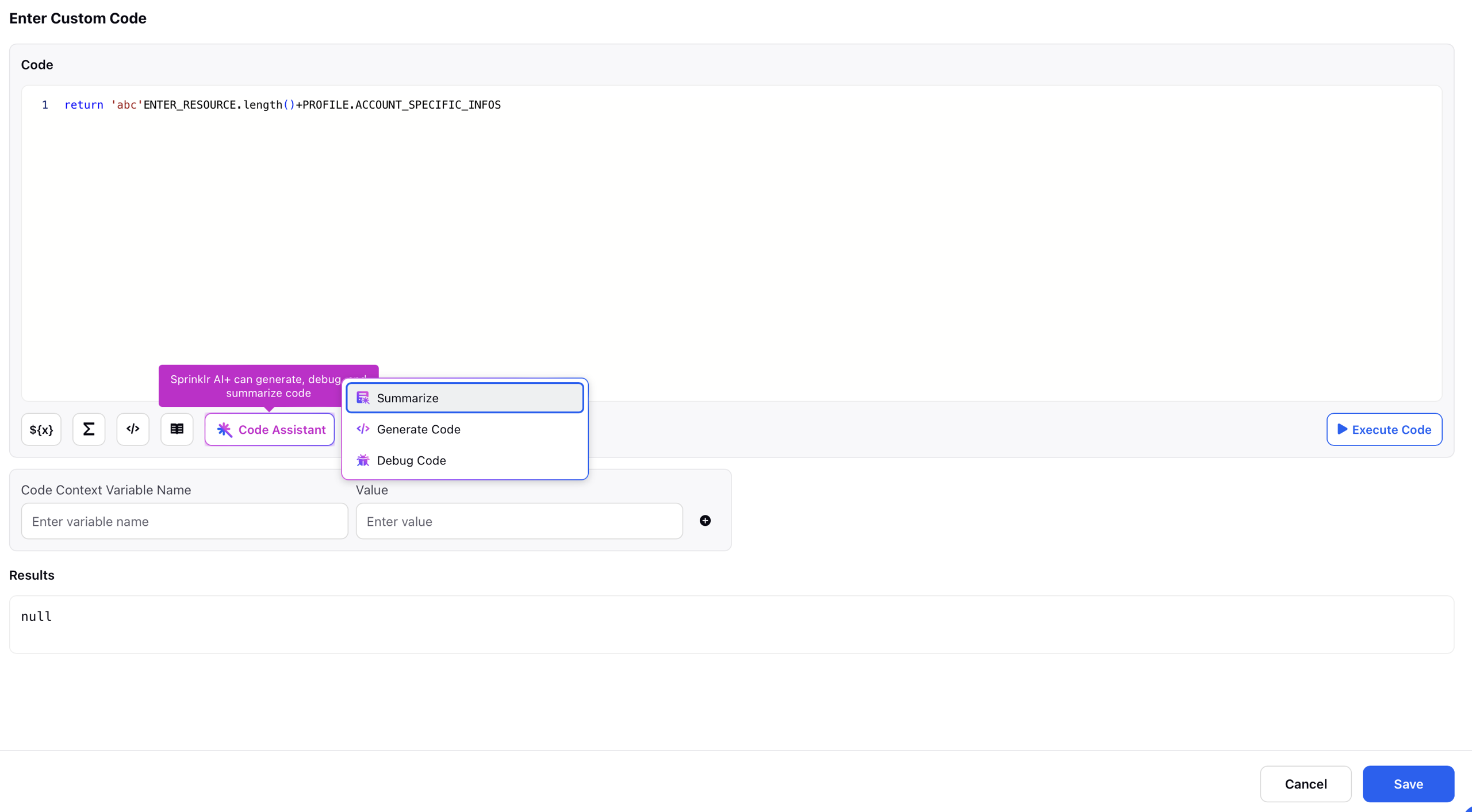
Code Assistant: The Code Assistant is a built-in support tool designed to help users write Groovy scripts more easily. It provides Summarize, Generate Code, and Debug Code capabilities for writing correct and efficient code. This is particularly useful for users who may be configuring workflows but lack detailed information on Groovy syntax or scripting logic.
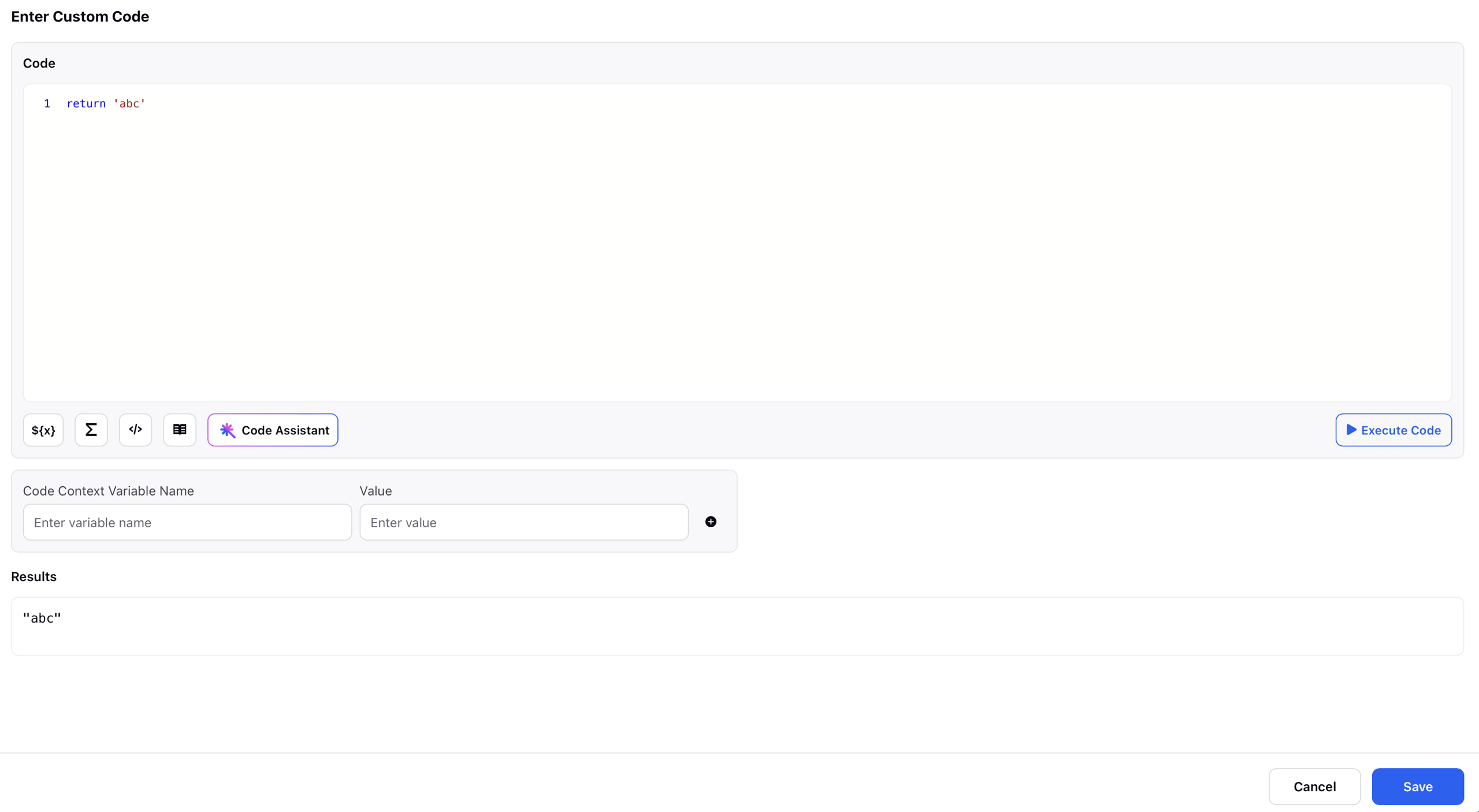
Execute Code: This feature allows users to test their Groovy scripts directly within the Custom Code Editor without running the entire workflow. By providing hard-coded values, users can simulate variable inputs and instantly see the expected output or any error messages. This is especially useful for debugging or validating logic, as it provides immediate feedback and helps ensure the script behaves as intended before being fully integrated into the workflow.
Result:
Error:
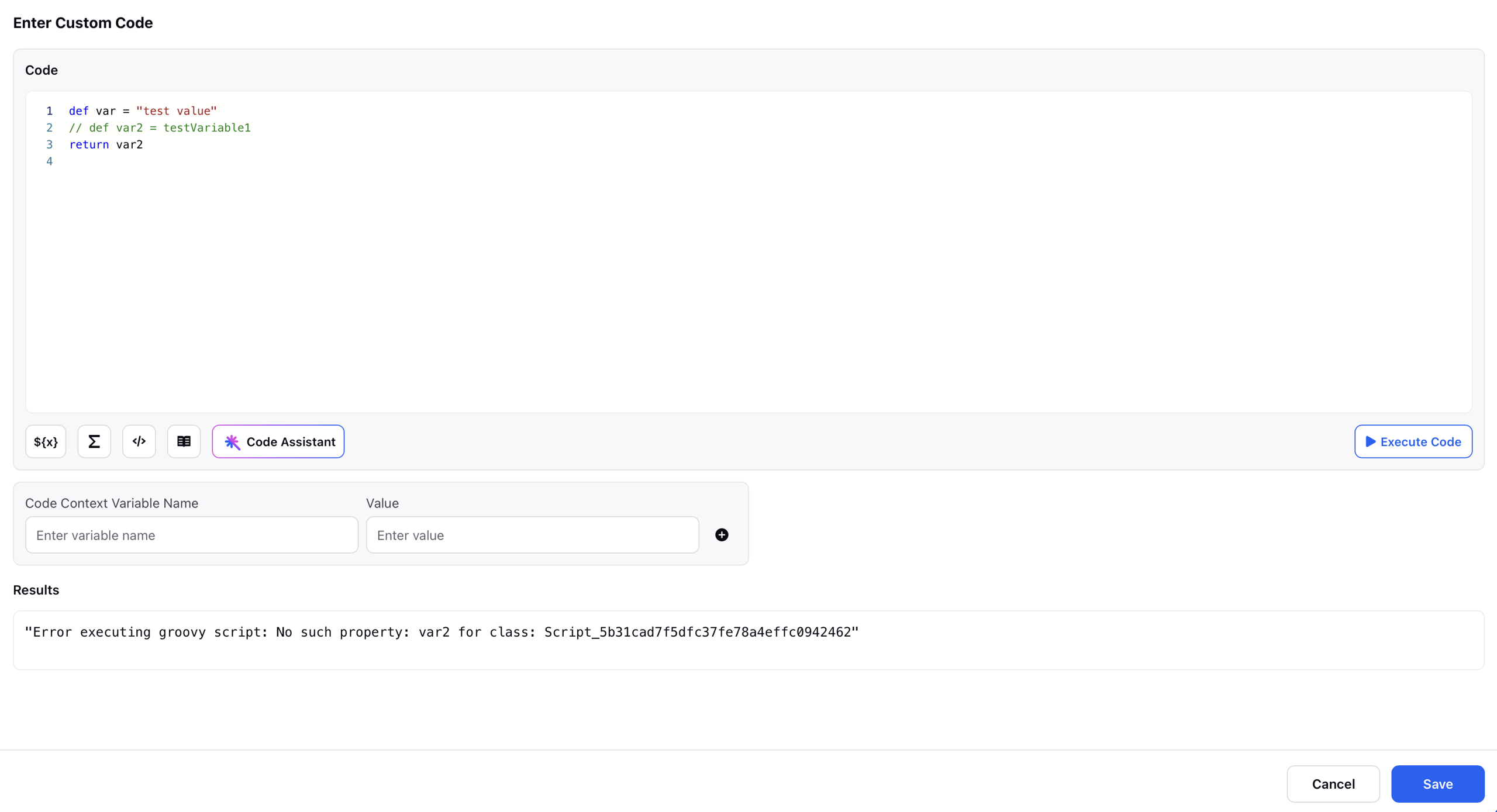
Code Context Variable: This field allows you define test values for variables referenced in your custom Groovy script.
The Custom Code Editor supports native data types when testing code using the Code Context Variable input.
You can pass complex data types like Lists, Maps, Booleans, and nested objects directly into the Code Context Variable input.